Data Encryption Standard Made With Key Sizes of 14 Bits
Today I would like to share you the power of cryptography.
I made this software 2011 in Eindhoven, Netherlands (country of cryptography) where I was having my exchange studies at the time.
The software is about the Data Encryption Standard or DES, however you like to call it.
DES With 14 Bits #
Data Encryption Standard is the old queen of cryptography, which eventually got caught for being too easy to solve. There is a great article in Wikipedia about the topic and how it has influenced modern cryptography.
What I did was kinda experiment if I could code this thing together with some tweaking to the original Standard. DES was created to encrypt with key sizes of 56 bits and block sizes of 64 bits doing 16 rounds of crypting in total.
To learn the standard and the basics of cryptography, I chose to do it with key sizes of 14 bits and block sizes of 16 bits doing 2 rounds of crypting in total. I actually succeeded on this and did a little software with Python to prove it.
Mathematics #
Here are the mathematics from my version of the Data Encryption Standard.
Permutations #
PC1 = [12, 5, 14, 1, 10, 2, 6,
9, 15, 4, 13, 7, 11, 3]
PC2 = [ 6, 11, 4, 8, 13, 3,
12, 5, 1, 10, 2, 9]
IP = [ 2, 14, 6, 10,
12, 8, 16, 4,
5, 13, 3, 9,
11, 1, 15, 7]
IP-1 = [ 14, 1, 11, 8,
9, 3, 16, 6,
12, 4, 13, 5,
10, 2, 15, 7]
E = [ 8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 1]
S = [
[ 4, 11, 2, 14, 15, 0, 8, 13, 3, 12, 9, 7, 5, 10, 6, 1,
13, 0, 11, 7, 4, 9, 1, 10, 14, 3, 5, 12, 2, 15, 8, 6,
1, 4, 11, 13, 12, 3, 7, 14, 10, 15, 6, 8, 0, 5, 9, 2,
6, 11, 13, 8, 1, 4, 10, 7, 9, 5, 0, 15, 14, 2, 3, 12],
[13, 2, 8, 4, 6, 15, 11, 1, 10, 9, 3, 14, 5, 0, 12, 7,
1, 15, 13, 8, 10, 3, 7, 4, 12, 5, 6, 11, 0, 14, 9, 2,
7, 11, 4, 1, 9, 12, 14, 2, 0, 6, 10, 13, 15, 3, 5, 8,
2, 1, 14, 7, 4, 10, 8, 13, 15, 12, 9, 0, 3, 5, 6, 11]
]
P = [ 6, 4, 7, 3,
5, 1, 8, 2]
Calculations #
We choose a sub key K’ of 12 bits
000110 110000
Calculations of F(R, K’) as R = 1011 0110
E(R) = 010110 101101
K (+) E(R) = 010000 011101
S7(B1)S8(B2) = 0011 1001
F(R, K') = 0101 1010
We choose a key K of 16 bits
0100 0110 0100 1001
And calculate the two keys K1 and K2
K+ = 0000 1110 0011 00
C0 = 0000111
D0 = 0001100
C1 = 0111000
D1 = 1100000
C2 = 1000011
D2 = 0000110
K1 = 001101000011
K2 = 100010101000
We choose an input I of 15 bits (e.g. the ASCI-coding of the characters ‘v’ and ‘b’)
0111 0110 0110 0001
And encrypt I using the DESHI-algorithm where we use the given IP and the calculated K1, K2 and IP-1.
IP = 1011 0001 0010 1011
L0 = 1011 0001
R0 = 0010 1011
R1 = L0 (+) F(R0, K1)
E(R0) = 100101 010110
K1 = 001101000011
K1 (+) E(R0) = 101000 010101
S7(B1) S8(B2) = 1100 0110
F(R, K’) = 1010 0101
R1 = L0 (+) F(R0, K1) = 0001 0100
L1 = R0 = 0010 1011
R2 = L0 (+) F(R1, K2)
E(R1) = 000010 101000
K2 = 1000010 101000
K2 (+) E(R1) = 100000 000000
S7(B1) S8(B2) = 0001 1101
F(R, K’) = 1100 1010
R2 = L1 (+) F(R1, K2) = 1110 0001
L2 = R0 = 0001 0100
R2L2 = 1110 0001 0001 0100
IP-1 = 1101 0100 1000 0100
Software #
Program is made with Python version 3.2. The program can probably be run if the system has 3.0 or newer version of Python, but only tested with 3.2. The latest version can be downloaded from: http://www.python.org/download/. The program can be used in Linux or Windows as long as there is Python installed into the system.
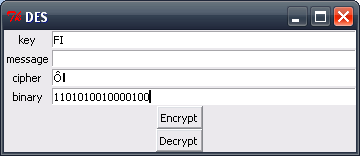
Here are some screenshots with the same examples as used in the earlier handwritten DES encryption.
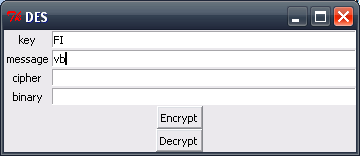
After clicking the encrypt button.

After clicking the decrypt button
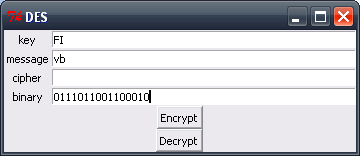
Usage #
This was just an experiment if I could learn DES and some cryptography, this software should not be used in real life situations. The method I used actually made DES weaker against attacks because I did it with less bits than the usual version. I hope maybe someone may find this information useful and maybe learn some cryptography. In my opinion it’s a really complex world and so much different from traditional software development, because of the mathematics that are included.
Source Code #
Here is the source code for this software. To run the software, just copy/paste the code into .py file and run it.
# GNU GPL
# des.py - Python version used: 3.2
from tkinter import * # UI tool import
from tkinter.messagebox import showerror # copies showerror
fieldnames = ('key', 'message', 'cipher', 'binary')
pc1 = [12, 5, 14, 1, 10, 2, 6,
9, 15, 4, 13, 7, 11, 3]
leftshifts = [3, 3]
pc2 = [ 6, 11, 4, 8, 13, 3,
12, 5, 1, 10, 2, 9]
ip = [ 2, 14, 6, 10,
12, 8, 16, 4,
5, 13, 3, 9,
11, 1, 15, 7]
e = [ 8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 1]
s = [
[ 4, 11, 2, 14, 15, 0, 8, 13, 3, 12, 9, 7, 5, 10, 6, 1,
13, 0, 11, 7, 4, 9, 1, 10, 14, 3, 5, 12, 2, 15, 8, 6,
1, 4, 11, 13, 12, 3, 7, 14, 10, 15, 6, 8, 0, 5, 9, 2,
6, 11, 13, 8, 1, 4, 10, 7, 9, 5, 0, 15, 14, 2, 3, 12],
[13, 2, 8, 4, 6, 15, 11, 1, 10, 9, 3, 14, 5, 0, 12, 7,
1, 15, 13, 8, 10, 3, 7, 4, 12, 5, 6, 11, 0, 14, 9, 2,
7, 11, 4, 1, 9, 12, 14, 2, 0, 6, 10, 13, 15, 3, 5, 8,
2, 1, 14, 7, 4, 10, 8, 13, 15, 12, 9, 0, 3, 5, 6, 11]
]
p = [ 6, 4, 7, 3,
5, 1, 8, 2]
ip1 = [ 14, 1, 11, 8,
9, 3, 16, 6,
12, 4, 13, 5,
10, 2, 15, 7]
def makeWidgets(): # makeWidgets function
global entries
window = Tk()
window.title('DES')
form = Frame(window)
form.pack()
entries = {}
for(ix, label) in enumerate(fieldnames): # creation of labels and entries into two columns
lab = Label(form, text=label)
ent = Entry(form, width=50)
lab.grid(row=ix, column=0)
ent.grid(row=ix, column=1)
entries[label] = ent
Button(window, text='Encrypt', command=en).pack(side=TOP) # encrypt button, click takes to function en()
Button(window, text='Decrypt', command=de).pack(side=TOP) # decrypt button, click takes to function de()
return window
def stringToBits(data): # string to bits function
data = [ord(c) for c in data] # creates unicodes to list
result = []
for ch in data:
i = 7
while i >= 0: # bit selection
if ch & (1 << i) != 0:
result.append(1)
else:
result.append(0)
i -= 1
return result # returns a list of created bits
def bitsToString(bits): # bits to string function
strinG = []
position = 0
a = 0
while position < len(bits):
a += bits[position] << (7 - (position % 8))
if (position % 8) == 7:
strinG.append(a)
a = 0
position += 1
return ''.join([chr(a) for a in strinG]) # returns a string of characters made from bytes
def permutate(table, block): # permutation function
return list(map(lambda x: block[x], table)) # returns the permutated list
def createSubkeys(key, pc1, pc2, leftshifts): # subkeys creation
key = permutate(pc1, [0] + stringToBits(key)) # pc1 permutation
i = 0
L = key[:7] # slices the permutation into LEFT and RIGHT
R = key[7:]
subkeys = []
while i < 2:
j = 0
while j < leftshifts[i]: # leftshifts the bits from beginning to end
L.append(L[0])
del L[0]
R.append(R[0])
del R[0]
j += 1
subkeys.append(permutate(pc2, [0] + L + R)) # pc2 permutation
i += 1
return subkeys
def des(message, ip, e, s, p, ip1, subkeys, crypt): # des function
if not message:
return ""
if len(message) % 2 != 0:
showerror(title='Error', message='The message or encrypted data must be a multiple of 16 bits!')
return ""
a = 0
result = []
while a < len(message):
cryptob = stringToBits(message[a:a+2]) # gets part of the string and turns it to bits
ipresult = permutate(ip, [0] + cryptob) # ip permutation
L = ipresult[:8] # slices the variable into LEFT and RIGHT
R = ipresult[8:]
if crypt == 'en': # sets the variables for the encryption or decryption
it = 0
itadd = 1
if crypt == 'de':
it = 1
itadd = -1
i = 0
while i < 2: # encryption
R2 = R[:]
R = permutate(e, [0] + R) # E permutation
R = list(map(lambda x, y: x ^ y, R, subkeys[it])) # XOR the permutation
B = [R[:6], R[6:]] # slices the permutation into list B[0] and B[1]
k = 0
bg = [0] * 8
position = 0
while k < 2:
f = (B[k][0] << 1) + B[k][5] # for clarification << means left shifting and >> right shifting
g = (B[k][1] << 3) + (B[k][2] << 2) + (B[k][3] << 1) + B[k][4]
h = s[k][(f << 4) + g] bg[position] = (h & 8) >> 3
bg[position + 1] = (h & 4) >> 2
bg[position + 2] = (h & 2) >> 1
bg[position + 3] = h & 1
position += 4
k += 1
R = permutate(p, [0] + bg) # P permutation
R = list(map(lambda x, y: x ^ y, R, L)) # XOR the permutation
L = R2
i += 1
it += itadd
ip1result = permutate(ip1, [0] + R + L) # ip-1 permutation
result.append(bitsToString(ip1result)) # adds the crypted part as string to result
a += 2
return ''.join(result) # returns result list as one joined string
def en(): #encrypt click
crypt_click('en')
def de(): #decrypt click
crypt_click('de')
def crypt_click(crypttype): #process of encryption or decryption depending of the click
key = entries['key'].get() # gets the key from the UI
if not key:
showerror(title='Error', message='You have to enter a key!')
else:
if len(key) % 2 != 0:
showerror(title='Error', message='The key must be 16 bits!')
else:
subkeys = createSubkeys(key, pc1, pc2, leftshifts) # creation of subkeys in createSubkeys() functions
if crypttype == 'en': # sets the variables to message or to cipher depending on what the user clicked
textfrom = 'message'
textto = 'cipher'
entries['cipher'].delete(0, END)
else:
textfrom = 'cipher'
textto = 'message'
messageOrCipher = entries[textfrom].get() # gets message or cipher
result = des(messageOrCipher, ip, e, s, p, ip1, subkeys, crypttype) # actual result from the des() function
binary = ''.join(map(str, stringToBits(result))) # makes the binary of the result
entries[textfrom].delete(0, END) # UI entry delete
entries[textto].insert(0, result) # UI entry insert
entries['binary'].delete(0, END)
entries['binary'].insert(0, binary)
window = makeWidgets() # creates the UI
window.mainloop() # mainloop of the UI to get actions